You are now leaving the aHUSSource.com website.
Alexion is not responsible for content included on third-party websites. Do you want to proceed?
Learn how complement system dysregulation occurs in atypical-HUS and how it could lead to TMA and progressive tissue damage so you can recognize the signs in your patients.
The complement system consists of a network of plasma proteins that protect against pathogens and foreign cells and maintain tissue homeostasis. Of the 3 pathways (classical, lectin, and alternative), the alternative pathway maintains a low level of baseline activity, and in healthy conditions, regulators on host cells help to control complement activation.6
In atypical-HUS, however, complement activation in the alternative pathway is dysregulated, which can be due to genetic mutations, polymorphisms, and autoantibodies. Triggers and other everyday occurrences amplify the complement system, and this uncontrolled constitutive activity can overwhelm native regulators and may lead to progressive and life-threatening complications.4,6

In atypical-HUS, complement dysregulation may be caused by:
Mutations in genes, including: C3, CFB, CFH, CFI, MCP, and THBD
Polymorphisms in genes, including: MCP, CFH, and CFHR1
Autoantibodies to CFH
*45% represents 119 of the 267 patients tested for ≥5 genes, from a registry of 851 patients.7
C3=complement component 3; CFB=complement factor B; CFH=complement factor H; CFHR1=complement factor H-related protein 1; CFI=complement factor I; MCP=membrane cofactor protein; THBD=thrombomodulin.
The number of new genetic abnormalities discovered in patients with atypical-HUS continues to increase over time.3,15-17 Regardless of whether or not a mutation is identified, patients with atypical-HUS have similarly devastating outcomes.3,14
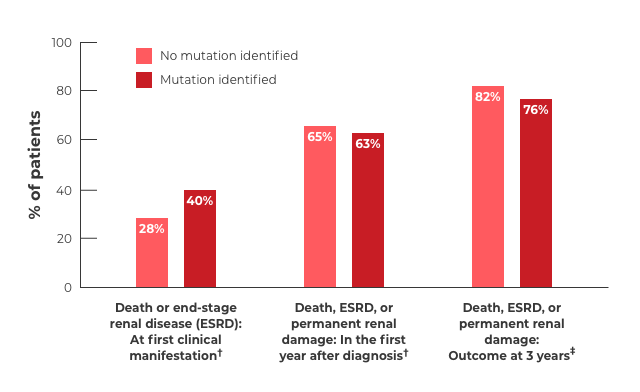
†Mutations consisted of MCP, CFH, and CFI. No mutation identified: n=81. Mutation identified: n=60.
‡Mutations consisted of MCP, CFH, CFI, C3, and THBD. No mutation identified: n=119. Mutation identified: n=116.